All The Planets In The Solar System Would Fit Between The Earth And The Moon

All the planets in the solar system would fit between the Earth and the Moon
More Posts from Scenesofspace and Others


Jennifer Daniel
Visualization of How Fast a Ball Drops on Various Solar System Bodies
This is an animation of how quickly an object falls 1 km to the surfaces of solar system objects like the Earth, Sun, Ceres, Jupiter, the Moon, and Pluto. For instance, it takes 14.3 seconds to cover that distance on Earth and 13.8 seconds on Saturn.
It might be surprising to see large planets have a pull comparable to smaller ones at the surface, for example Uranus pulls the ball down slower than at Earth! Why? Because the low average density of Uranus puts the surface far away from the majority of the mass. Similarly, Mars is nearly twice the mass of Mercury, but you can see the surface gravity is actually the same… this indicates that Mercury is much denser than Mars.
(via @thekidshouldsee)




The last shuttle

Today NASA released parts of the set of highest-resolution pictures of Pluto from the New Horizons probe’s fly-by in July. As they write, “these latest images form a strip 50 miles (80 kilometers) wide on a world 3 billion miles away.” Imagine that. They are also the highest resolution images we’ll have of Pluto in a long, long time.
This picture, a crop, shows Sputnik Planum and the al-Idrisi mountains, which are made of big chunks of water ice. Be sure to check out the whole thing.
Watch a NASA Spacecraft Touch Down On an Asteroid to Collect a Sample
On Tuesday, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft touched down on an asteroid called Bennu for about six seconds in order to collect a mineral sample to bring back to Earth.
The Origins Spectral Interpretation Resource Identification Security - Regolith Explorer spacecraft will travel to a near-Earth asteroid, called Bennu (formerly 1999 RQ36), and bring at least a 2.1-ounce sample back to Earth for study. The mission will help scientists investigate how planets formed and how life began, as well as improve our understanding of asteroids that could impact Earth.
The video above is a time lapse sequence of the touch down, sampling, and subsequent take off.
These images were captured over approximately a five-minute period. The imaging sequence begins at about 82 feet (25 meters) above the surface, and runs through the back-away maneuver, with the last image in the sequence taken at approximately 43 feet (13 meters) in altitude – about 35 seconds after backing away. The sequence was created using 82 SamCam images, with 1.25 seconds between frames.
Space Robot Roll Call
Emily Lakdawalla of the Planetary Society filed a report on humanity’s current roster of spacecraft currently exploring the solar system (and beyond).
Chang'e-4 and Yutu-2 are now past their prime mission and are in their extended mission phases. Their companion SmallSat, Longjiang-2, will crash into the Moon on 31 July to bring its mission to an intentional end. Parker Solar Probe is near aphelion as of 1 July and will reach its third death-defying solar perihelion on 1 September. BepiColombo completed its near-Earth commissioning phase on 5 April and is now settling into its long-cruise phase. Earlier this year, the ESA-JAXA Mercury mission was racing ahead of Earth on an inside track, but its elliptical orbit has now taken it farther from the Sun than Earth, allowing Earth to catch up. It will return to Earth’s neighborhood in April 2020 for a flyby.
I counted roughly 30 different probes and rovers in operation, most of them gathered around the Moon and Mars. Sure, where’s my jetpack and flying car and all that, but the fact that humanity has more than two dozen robots currently exploring the solar system seems pretty futuristic to me.
Wikipedia also has a page listing currently active probes and of course there’s the lovely & informative spaceprob.es as well.






Space cards
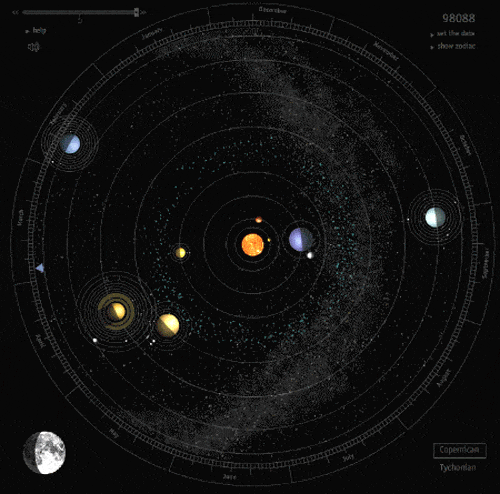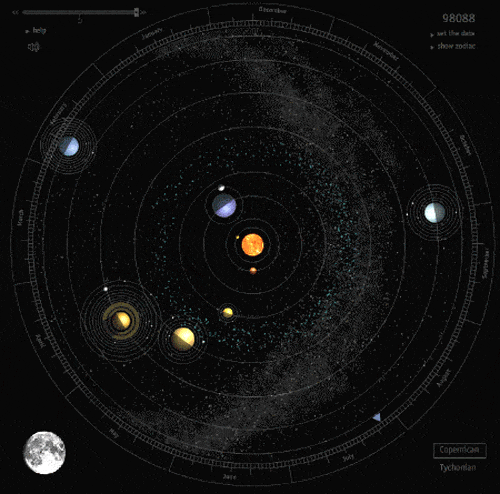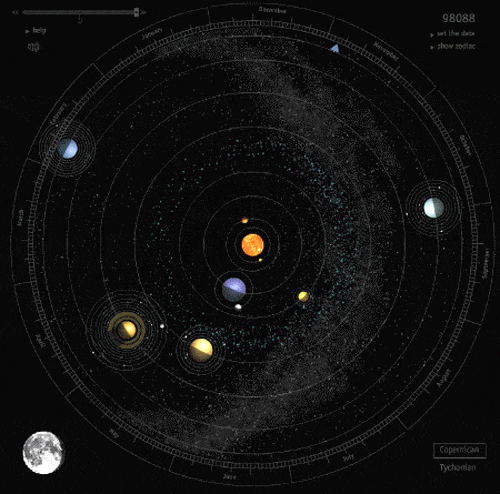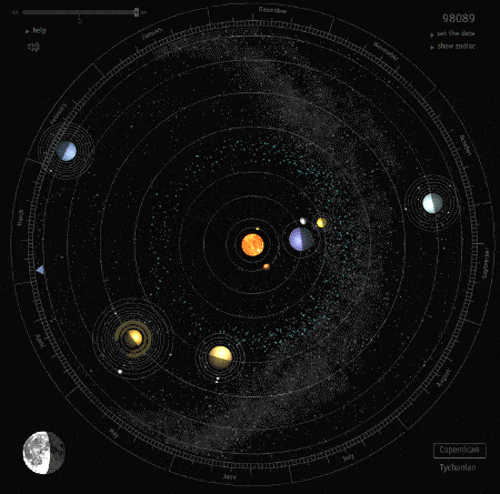
There Are Way More Rogue Planets Than We Thought
The galaxy is wild. Our solar system, with its surprising abundance of living creatures and nonstop radiation and asteroid showers, is a placid, private garden compared to the rest of it.
In particular, there are perhaps trillions of rogue planets (planetary bodies ranging from little rocky Earth-sized guys to super-Jupiter gas giants) in the Milky Way, including a surprisingly large fleet of the things right near the galactic core.
This is unusual, since the typical way we detect exoplanets is by marking their repeated procession across a star. But rogue planets, by definition, don’t orbit stars. So the way astronomers find them is a little different, requiring use of gravitational microlensing.
Gizmodo breaks it down:
Data gathered by NASA’s now-retired Kepler Space Telescope has revealed a small population of free-floating planets near the Galactic Bulge. The new finding raises hope that a pair of upcoming missions will result in further detections of unbound planets, which drift through space separated from their home stars….
It’s impossible to know what the conditions are like on these presumed rogue exoplanets, but [astronomer Iain] McDonald said they could be “cold, icy wastelands,” and, if similar in size to Earth, their surfaces would “closely resemble bodies in the outer Solar System, like Pluto.”
The new paper suggests the presence of a large population of Earth-sized rogue planets in the Milky Way. It’s becoming clear that free-floating planets are common. McDonald said his team is currently working to come up with a more precise estimate for how many of them might exist.
Did you catch that part about how McDonald’s team made this discovery using a now-retired telescope? Yeah. Apparently the new telescope projects coming online are both more powerful and (in particular) better equipped to detect gravitational lensing effects, and therefore more likely to detect rogue planets in the future.
The Sweden Solar System
Spanning from comets in the south to the termination shock zone in the northern part of the country, The Sweden Solar System is a scale model of the solar system that spans the entire country of Sweden, the largest such model in the world.
The Sun is represented by the Ericsson Globe in Stockholm, the largest hemispherical building in the world. The inner planets can also be found in Stockholm but the outer planets are situated northward in other cities along the Baltic Sea.
-
 albad liked this · 3 years ago
albad liked this · 3 years ago -
 stray70 reblogged this · 3 years ago
stray70 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 stray70 liked this · 3 years ago
stray70 liked this · 3 years ago -
 piccolipezzi liked this · 3 years ago
piccolipezzi liked this · 3 years ago -
 deepcleaningcorona reblogged this · 5 years ago
deepcleaningcorona reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 rh35211 reblogged this · 6 years ago
rh35211 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 aimeramare liked this · 7 years ago
aimeramare liked this · 7 years ago -
 floating-plants reblogged this · 8 years ago
floating-plants reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 superalk reblogged this · 8 years ago
superalk reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 superalk liked this · 8 years ago
superalk liked this · 8 years ago -
 whatsthatlookfor reblogged this · 8 years ago
whatsthatlookfor reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 coronanoctis reblogged this · 9 years ago
coronanoctis reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 scenesofspace reblogged this · 9 years ago
scenesofspace reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 ambrosehistoryof reblogged this · 9 years ago
ambrosehistoryof reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 aubreyferrencestationgq reblogged this · 9 years ago
aubreyferrencestationgq reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 amyrutherford reblogged this · 10 years ago
amyrutherford reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 a-nobella liked this · 10 years ago
a-nobella liked this · 10 years ago -
 myfavworks liked this · 10 years ago
myfavworks liked this · 10 years ago -
 diruel reblogged this · 10 years ago
diruel reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 waddledee18 reblogged this · 10 years ago
waddledee18 reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 static-stars liked this · 10 years ago
static-stars liked this · 10 years ago -
 static-stars reblogged this · 10 years ago
static-stars reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 celestialmunkee liked this · 10 years ago
celestialmunkee liked this · 10 years ago -
 celestialmunkee reblogged this · 10 years ago
celestialmunkee reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 catherinesolo reblogged this · 10 years ago
catherinesolo reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 blueferry-blog liked this · 10 years ago
blueferry-blog liked this · 10 years ago -
 iceydeathtousall reblogged this · 10 years ago
iceydeathtousall reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 megajaco liked this · 10 years ago
megajaco liked this · 10 years ago -
 jonesgirl88 liked this · 10 years ago
jonesgirl88 liked this · 10 years ago -
 lcmom-blog liked this · 10 years ago
lcmom-blog liked this · 10 years ago -
 mudshark58 reblogged this · 10 years ago
mudshark58 reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 needstosortoutpriorities reblogged this · 10 years ago
needstosortoutpriorities reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 kkjaatun reblogged this · 10 years ago
kkjaatun reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 amansremains-blog liked this · 10 years ago
amansremains-blog liked this · 10 years ago -
 j-a-m-i-e-thats-me reblogged this · 10 years ago
j-a-m-i-e-thats-me reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 princessofbadassery reblogged this · 10 years ago
princessofbadassery reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 notthedogs liked this · 10 years ago
notthedogs liked this · 10 years ago -
 cottonwoolfairy liked this · 10 years ago
cottonwoolfairy liked this · 10 years ago -
 thepicklesfromlasttime reblogged this · 10 years ago
thepicklesfromlasttime reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 thepicklesfromlasttime liked this · 10 years ago
thepicklesfromlasttime liked this · 10 years ago -
 shutupmanda liked this · 10 years ago
shutupmanda liked this · 10 years ago -
 starry-puddles reblogged this · 10 years ago
starry-puddles reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 starry-puddles liked this · 10 years ago
starry-puddles liked this · 10 years ago -
 mickeyslovelyminnie-blog liked this · 10 years ago
mickeyslovelyminnie-blog liked this · 10 years ago -
 itsjonny456-blog liked this · 10 years ago
itsjonny456-blog liked this · 10 years ago